About
Landing in master, plasma has an optional new startup method to launch and manage all our KDE/Plasma services via a systemd user instance rather than the current boot scripts. This will be available in Plasma 5.21.
It is currently opt-in, off by default. I hope to make it the default where available after more testing and feedback, but it is important to stress that the current boot-up method will exist and be supported into the future. A lot of work was put into splitting and tidying so the actual amount of duplication in the end result is quite small and managable.

Motivation
Overlapping requirements
We have to start a lot of things in a given order. Systemd naturally is designed for handling doing this.
Whilst we already have a somewhat working system, it has issues. One classic problem is services that talk to other services needing to be both spawned but also fully initialised before the other can send a message. DBus activation solves a lot; but not quite enough.
For example, we have the real world case of scripts run long before plasmashell trying to send notifications; we want DBus daemon to know our notification server it's activatable so that it will pause the dispatch of the message, but making it DBus activatable can't guarantee the dependencies are run in the correct order. This is currently solved with a genius horrific hack.
But starting things up is only half the battle. We currently have a big issue with shutting things down. Whose responsibility is it to stop running services? A lot of things only exit because their wayland connection is swept away. When dealing with services that potentially restart during the session lifespan, this solution is far from trivial and the current situation is fundamentally broken.
Customisation / Sysadmin Familiarity
Most users and especially sysadmins already have to learn how to use their init system. Whether it's simply enabling a service on boot, or something much more complex users are exposed to it already. If not, there is good existing documentation and countless Stackoverflow posts to answer any question.
We had a meeting akademy 2 years ago about use of systemd and it was the sysadmins from Limux who clearly knew far more than any programmer as to how it should all work. There is a lot more merit in using existing things than just sharing code.
Another big motivating factor was the ability for customisation. The root of Plasma's startup is very hardcoded. What if you want to run krunner with a different environment variable set? or have a script run every time plasmashell restarts, or show a UI after kwin is loaded but before plasma shell to perform some user setup? You can edit the code, but that's not easy and you're very much on your own.
Systemd provides that level of customisation; both at a distro or a user level out of the box. From our POV for free.
CGroups and resource limits
I've talked about use of cgroups for applications for better control of resources. Especially as more things become multi-process.
CGroups and slices provide several benefits over what we can do currently. Because resources are always relative to within the parent slice, we are able to boost resources as well as limit things. This will allow us to bump kwin and such ever so slightly without needing elevated cap privileges.
This also works the other way; cgroups have some extra scheduler features not otherwise available. We can not just set weigh to a process, but also absolute limits. This could be useful for file indexers and alike to minimise battery drainage or capture runaway processes. CGroups are where all the new kernel features are.
Memory management is another factor, when we run out the kernel comes in and kills some processes.
We can tag some services as being safer to OOM kill than others with a lot more granularity than a single oomscore adjustment. We can provide expected memory usages for a service, we can put defaults levels on entire slices at once, and it's all easily customisable by the user if their opinions don't match our upstream defaults.
Logging
The current state of logging is a mess. One of two things happen:
Either stderr from a service is lost, or logs go into one giant "xsession-errors" file. This file exists on a real file system slowly expanding and expanding. It doesn't rotate, if it gets too big your home folder becomes full and things explode. Each time you log in, we override that log, so we lose any history.
The alternative is that logs are simply lost.
Systemd provides queryable logging with each unit, and each invocation of each unit being separate. It's already making my life a lot easier for the last bugs I've been working on. When people on bugzilla have this too, it'll make everything easier.
The road to get here
Previous implementations
A plasma systemd boot has been tried before by Elias Probst. It worked well as a demo, and was used as inspiration for some parts. The key difference now is instead of trying to design around plasma, we're changing plasma to fit what we need and really put the focus on every last detail.
Refactor, Split, Refactor, Split, ...
Unintuitively the first start of a port to systemd was a complete rewrite of the legacy path.
Plasma used to be managed by a tree of processes that would spawn, set up some environment variables, spawn the next part of the boot and continue running. We eventually get to ksmserver, which was a monolith that did many many things. It started several hardcoded processes like kwin, then all the autostart .desktop files, and then session restore. There were many reasons to break this up that I outlined when I started in 2018.
Since then we've been chopping a tiny part out every release. Each release would split out a tiny part at a time so we could always be on top of any regressions that happened.
Once we'd refactored and rewrote some parts we could have a very clear and readable understanding of what actually happens in a plasma boot and what is really dependent on what.
The biggest problem that we have is many things rely on environment variables or even xrdb databases to be correct at the time of launching; several early parts of the boot (kcminit, kded phase0) will adjust these and the next parts may rely on these for correct theming.
Another massive rewrite that landed (by Kai Uwe Broulik) was the detaching of kwin from ksmserver. kwin needs to know which session we're restoring so that restored windows can be placed at the right place; this previously came from an environment variable that means we needed ksmserver up and running to spawn kwin. We rewrote how that all works and gets communicated so the order can be agnostic but still without any features getting lost.
Final patchset
Eventually we got to a point where ksmserver is only dealing with X11 session management. We have another quite tiny binary (plasma_session) that only deals with starting services in a specific order. And everything else is completely separate standalone independent components. This has been released for a while. Even without the systemd boot, everything is in a much much cleaner better off state.
The final patch to use systemd is then really quite boring and small. We just don't call the plasma_session binary, and instead try to start a systemd target; plasma-workspace.target.
All our core services ship their own .service files which plasma-workpace requires for a full Plasma session.
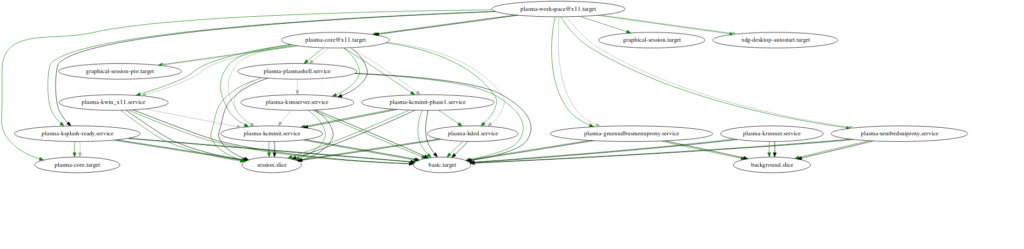
Autostart files
One of the key aspects of startup is handling autostart .desktop files in /etc/xdg/autostart or ~/.config/autostart. We need this to work as before.
Benjamin Berg (of Red Hat and Gnome) came up with a very elegant solution using a systemd generator. It goes through all the .desktop files parsing them and generates an appropriate systemd service automagically.
For application developers everything keeps working the same, but to an end user we can interact with them like native services. We get the best of both worlds.
Despite being a shared implementation even KDE-specific things like X-KDE-AutostartCondition just work. Implementation wise the generator converts this into an ExecCondition= line which then calls into a plasma-shipped binary to check if it's allowed.
Current state
Is it faster?
A lot of the prep work over the past few years to get to this state has made absolutely massive differences. The splitting found bugs dead code and potential optimisations that add up to magnitudes of difference.
As for switching over to the systemd itself, it should be roughly the same. Ultimately we're triggering the exact same set of things in the exact same order with the exact same blocks if we've done our job properly. Sorry to disappoint!
Is it finished?
The fundamentals are definitely at a point that I think are stable and working; but we haven't enabled all of the potential extra features we have available. I would welcome people who are experiences to give feedback and help out.
Enabling
You must have latest master of Plasma, it is not in the 5.20 beta.
Enable with:
kwriteconfig5 --file startkderc --group General --key systemdBoot true
As mentioned above there are checks that you have the systemd 246 or newer for the generator of existing autostart services to work.
To confirm the boot worked correctly you can run
systemctl --user status plasma-plasmashell.service
It should show as active.
This safety check of 246 can be skipped. You will lose auto-activation of apps using the classic .desktop file approach, but everything else still works. I won't mention how publicly to avoid false bug reports, but as a dev you can probably find out.
Dev setups - a caveat
If you build your own KDE and install into a non standard prefix, instead of getting Plasma from your distribution, there is one new hurdle. Systemd user sessions starts earlier than most people set their custom prefixes so naturally it can't find things in your new paths.
There are multiple solutions, simplest is to re-run ./install-sessions script in plasma-workspace which contains a workaround for systemd to find services.
Wrap Up
A lot of the work done to get to this stage has been extremely beneficial to all users regardless of whether they end up actually using this. We fixed and cleaned so much along the way.
I strongly believe the benefits it offers are very real, and look forward to hearing feedback from users using it.
If you do have any issues please do reach out to me in the usual channels.